Own Materials
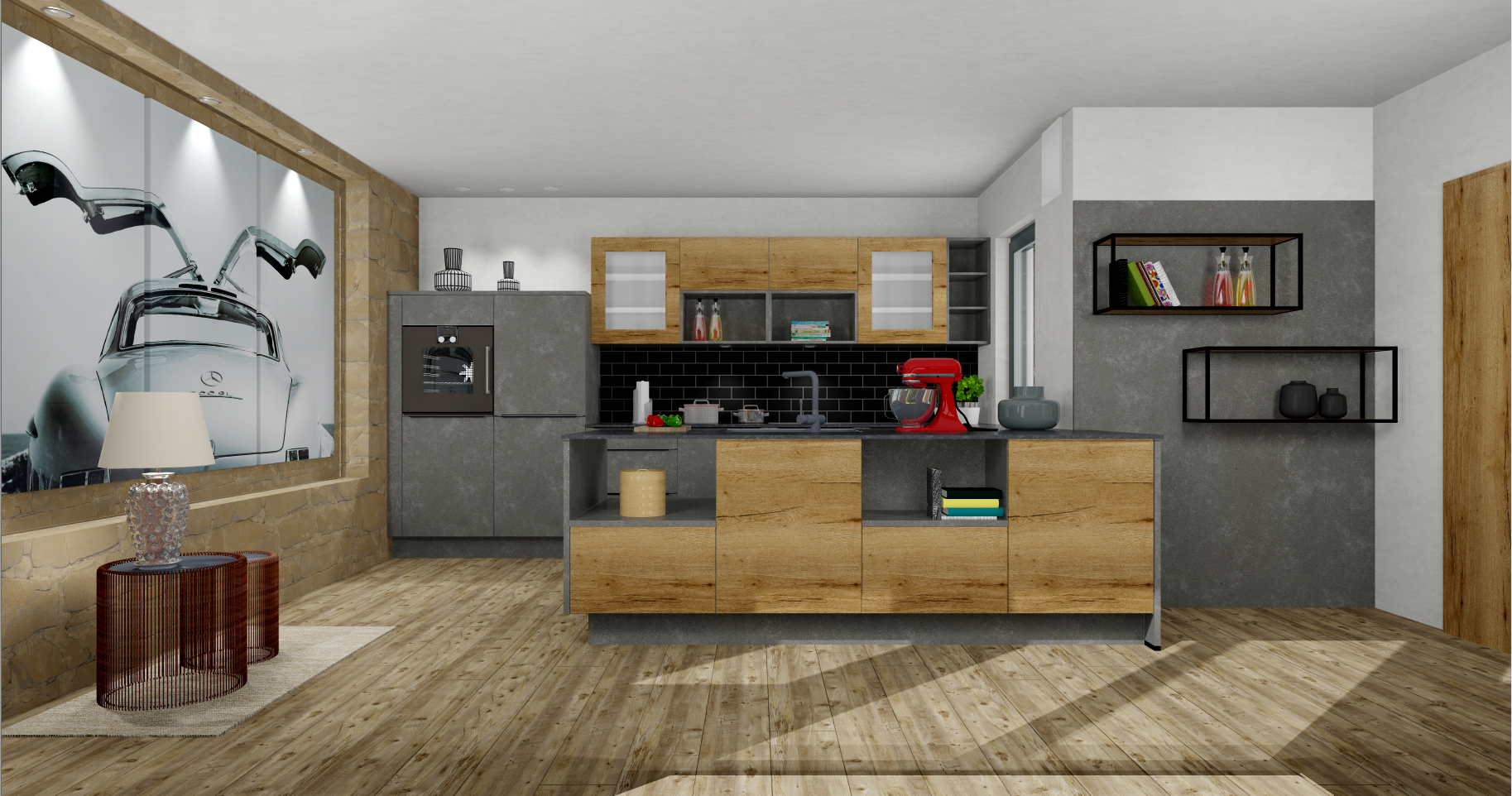
With the CARAT installation you automatically have access to a large number of neutral textures In computer graphics, one uses textures as surfaces of a 3D models., patterns and background images, that you can use for the further design of room elements, such as walls, floors, windows as well as for the many diverse construction articles and decoration articles. Despite the abundance of colours and patterns, it can occur however that for a particularly creative room design a specific colour, a special pattern or a certain background image, is missing.
So that your creativity is not limited within this range, you can if necessary store your own textures, so-called Own Materials, in a special fixed directory available to you. Since you can use the own materials in the most diverse areas, it results in numerous application possibilities.
Possible Applications for Own Materials
- Extraordinary textures and patterns for an even more unique room design.
- Real pictures as window Programs and files are shown in so called windows in the operating system of the same name. In CARAT each view (e.g. floor plan, article input, front view, perspective etc.) opens its own window. Multiple windows can be shown simultaneously for processing. If changes are made in one of these windows, this has an automatic effect on all other windows. background.
- Creating of a personal window foreground (with transparent areas).
- Pictures of special appliances or sinks.
BMP Windows bitmap (BMP) is a two-dimensional raster graphics format, which was developed for the operating system Microsoft Windows and OS/2, and was introduced with Windows 3.0. The file-extension is *.bmp., TIFF TIFF or TIF (Tagged Image File Format) is a file format for saving image data. The TIFF format was originally developed by Aldus (taken over by Adobe in 1994) and Microsoft for scanned raster graphics for colour separation. and JPG JPEG or JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a committee of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) founded in 1986. In September 1992 the committee developed a standardized procedure for a lossy compression of digital (natural) photographic images, that was subsequently named for them. JPEG is the most common photo format on the Web. are supported as image formats The format or formatting (Latin, forma) is designated in word processing as the design of the text document. In this case meaning the selection of character fonts and character style such as bold or italics., which can be created with every good graphic program. Using your graphics program, you have the ability to scan from a sample of any plain colour or special pattern, or even use self photographed images, to create a texture for your own materials.
Information about the image formats supported
Windows bitmap BMP is a two-dimensional raster graphics A raster graphic, also named pixel graphic (Bitmap), is a way to describe an image in a data form readable by computers. Raster graphics exist of arrangements of pixels (picture points) in a grid form, each being assigned a colour. The key features of a raster graphic are the width and height in pixels, also know as resolution, as well as the colour depth. format, which was developed for the operating system An operating system is the software which enables the use of a computer. It administrates operating resources like memory, input and output devices and controls the execution of programs. Microsoft Windows and OS/2, and was introduced with Windows 3.0. The file-extension is *.bmp.
Advantages
- BMP supports colour depths The colour depth is given in bits, and gives information about how many colour tones a single pixel can be assigned. The colour depth indicates thus the refinement of the colour shades. from 1 to 24 Bit (max. 16.777.216 colours).
- The BMP-format is widely compatible with existing Windows programs, especially with older versions.
- BMP-files are suitable for Windows background images.
Disadvantages
- BMP does not support data compression, which results in very large file sizes.
- JPEG JPEG or JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a committee of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) founded in 1986. In September 1992 the committee developed a standardized procedure for a lossy compression of digital (natural) photographic images, that was subsequently named for them. JPEG is the most common photo format on the Web. or TIFF files are commonly more suitable for pictures in photo-quality.
- BMP is not suitable for websites or e-mail-attachments.
- BMP-files are not supported by web browsers.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group), JPEG-graphics store a single raster graphic in 24-Bit-colour (maximum 16.777.216 colours). JPEG is a format independent from platforms, that supports the greatest possible compression, it is however very lossy. The JPEG-compression was developed for natural pictures (raster graphics). These are pictures one finds in the photography or with pictures generated by computers. JPEG is not suitable for digital line drawings (for example for a screenshot or a vector graphic A vector graphic is a computer image, that is made up of primitive graphics like lines, circles and polygons. For example, to save the image of a circle, a vector graphic requires a minimum of two values: the location of the centre point of the circle, and its diameter.), which contains many adjoining pixels Pixel or picture element identifies both, the smallest unit of digital raster graphics and the display of these graphics on a monitor with raster activation. with exact identical colour values, few colours and sharp edges. For those pictures are the formats BMP, TIFF or PDF The Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF) was developed and perfected in the 80's by Adobe Systems. Adobe PDF files contain data from any application, that can be displayed on every computer, and are suitable thereby to be exchanged with users throughout the world. better suitable by far.
Advantages
- With photographic or photo-realistic picture-material a higher compression is supported.
- The variable In CARAT, variables are wild cards that are used for different values and percent values, since the actual value changes, depending on the respective commission. By employing a variable in a document, for example a text for the VAT, can the VAT amount be supplemented with a wild card. When printing the document, the respective VAT amount will then be displayed in the location of the wild card. compression allows optimal regulation of the file size.
- JPEG is an extensively supported internet-standard.
Disadvantages
- This lossy compression leads to a loss of quality of the original picture-data.
- If you modify JPEG-files and store them again, the loss of quality increases compared to the original picture data.
- JPEG is not suitable for simple graphics with few colours, wide monochromatic areas or intense differences of brightness.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a file format, which is able to store a graphic in any colour depth. TIFF is probably the most supported graphic file format in the printing industry. Optional The word option (from Latin: optio = free will) used in computing means a choice. In CARAT it is normally used with a list box. compression is supported, but it is not suitable for being displayed in web browsers. TIFF is, besides PDF, an important format for exchange of data in the pre-press at publishing houses and print shops. In the internet is the TIFF-format used to provide high-resolution pictures in printable, lossless quality to the users, e.g. publishing houses. At the same time is accepted, that these files have the multiple size than a lossy compressed JPG-picture.
Advantages
- Due to its good quality is TIFF foremost suited for print products.
- TIFF is an extensively supported format, especially between Macintosh and Windows computers.
- Optional compression is supported.
- The expandable format supports various optional functions.
Disadvantages
- TIFF is not supported by web browsers.
- The expandability results in many different TIFF graphic-types.
- Not all TIFF-files are compatible with all programs supporting the basis TIFF-standard.
In general, you should adjust the size of a texture to the image contents or the intended purpose. With plain coloured textures a very small image size is sufficient, with Intricate patterns a certain repeat should be maintained, in order to avoid an unpleasant tile effect. For real images, like for example illustrations of appliances or sinks, you should pay attention to aspect ratio, so that these images are not shown distorted in the plan. In general, you should save the scanned images or images taken with a digital camera, in such a way that you maintain a good compromise between optimal quality and smaller file size.
Overview of the image/file sizes
|
Image size |
File size |
|---|---|
|
(in pixels) |
(as BMP) |
| 64 x 64 | ca. 10 KB 1 KB (Kilobyte) (1.000 Byte) A unit to indicate the total available memory capacity. One byte means an addressable memory unit, which has the capacity to store any character, e.g. A, B, C... |
| 512 x 128 | ca. 200 KB |
| 512 x 256 | ca. 400 KB |
| 512 x 384 | ca. 600 KB |
| 512 x 512 | ca. 750 KB |
| 512 x 1024 | ca. 1.5 MB 1 MB (Megabyte) (1.000.000 Byte) A unit to indicate the total available memory capacity. One byte means an addressable memory unit, which has the capacity to store any character. |
| 1024 x 1024 | ca. 3 MB |
All textures that you want to use for your own materials, must be saved in the USERMAT directory, which is found in the CARAT main directory. You can use up to 20 alphanumeric An alphanumeric character is in the narrow sense either a letter or a number. The term is used in telecommunications and computer technology. characters for the file name. The order that results from the file names, later also determines the order in which the textures are shown in CARAT. So that you can organize your textures better, you have the possibility to sort your textures into any number of sub-directories within the USERMAT directory.

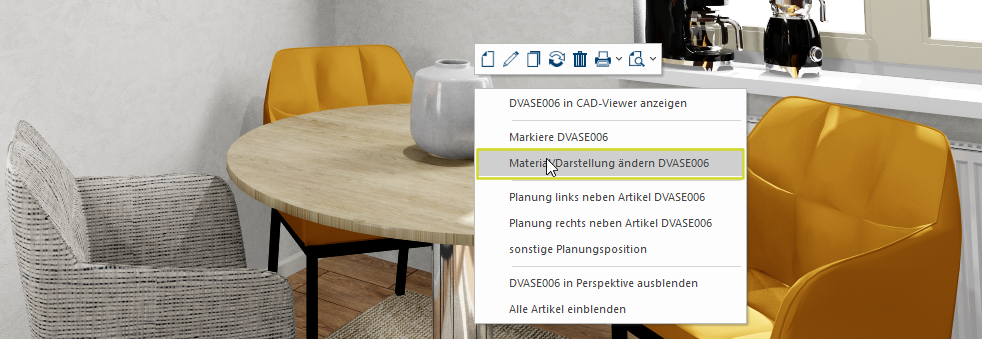
After you have saved your own textures in the USERMAT directory, you can use these via the perspective window. For this, please first move your mouse pointer in a surface of an article in the perspective window, for which you want to edit the texture. Then click Typically the LEFT mouse button is pressed once quickly, if not specified differently. Clicking will either mark an object, or when clicking on a button, the execution of the desired activity (e.g. OK, Cancel, Close). with the right mouse button In dialogue windows you always find one or more buttons that can be activated by clicking on them. Typical functions for buttons are e.g. OK, Cancel, Apply. Buttons are always activated by a single click with the left mouse button. to open the context menu In almost all Windows programs a click with the RIGHT mouse button opens a context menu containing a list of commands that are commonly the next step of a procedure..
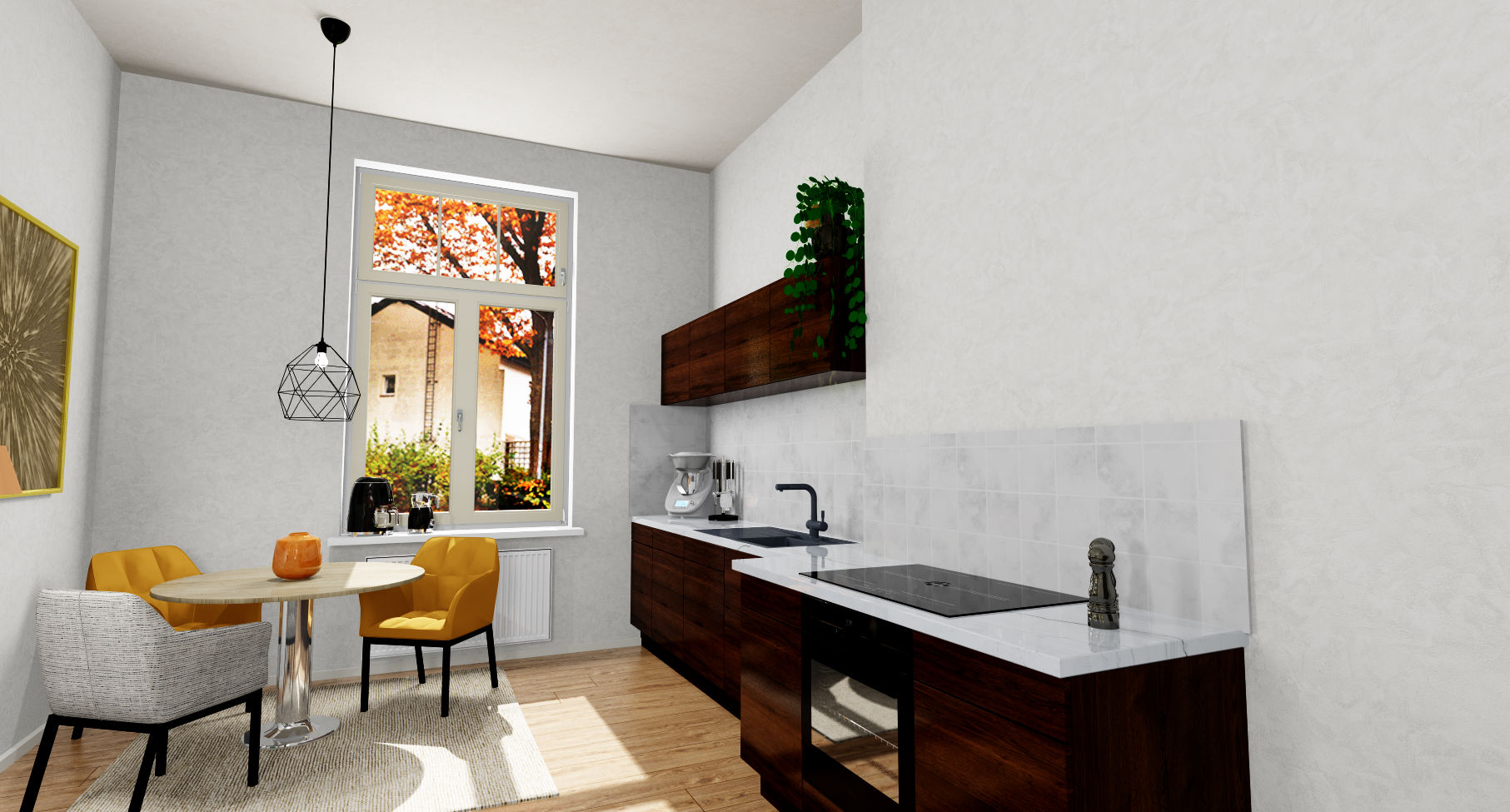
Example: The texture of the vase is to be changed in perspective. Right click on the surface of the vase to open the context menu. There you select the option Edit material/design ....
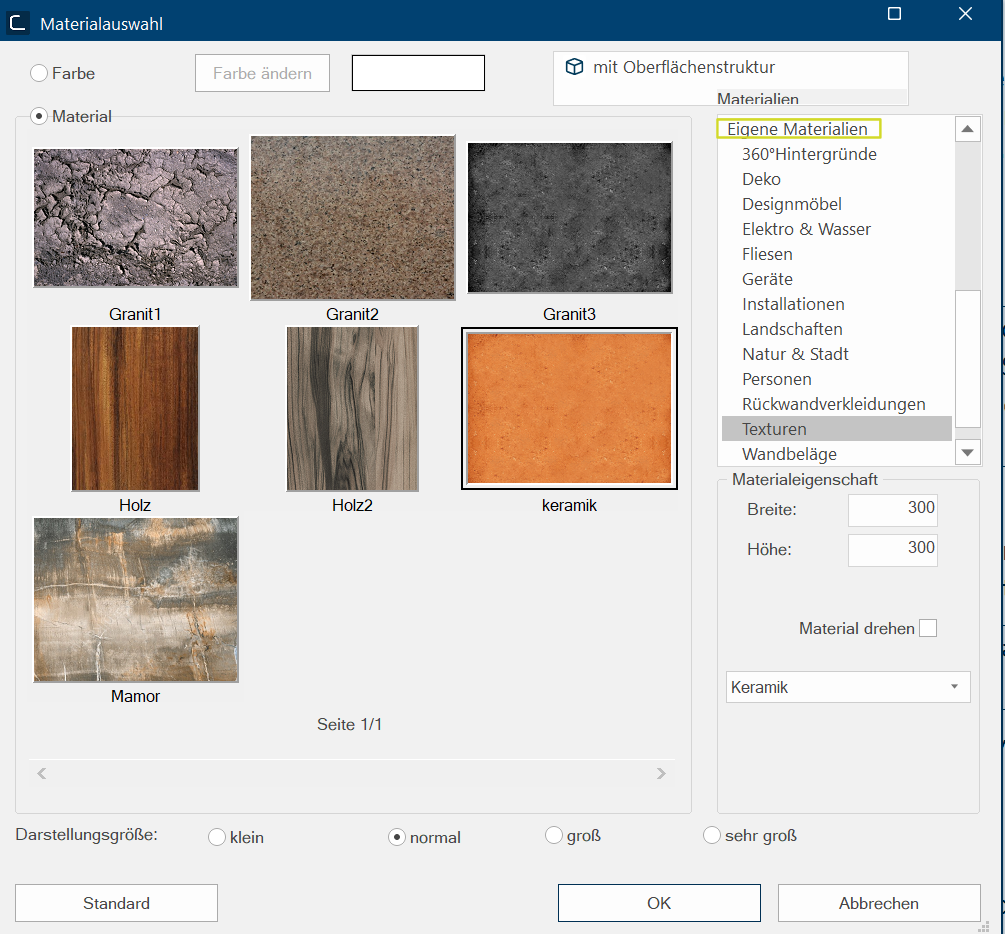
A new dialogue Dialogue, dialogue windows or dialogue fields are special windows in software applications. Dialogue windows are displayed by application programs in different situations to request input or confirmation from the user. opens. Here you select the Own materials group in the Materials area and there the appropriate directory. Here you can also specify how large the selected texture is to be displayed in the design. You can also specify whether the material is to be rotated. You can also set a material property for the selected texture here, so that the texture appears more matt or glossy.
To select a texture, mark the desired texture and click subsequently on the OK button. Then you will see the edited texture in the perspective.
After that, save again the planning in CARAT.
You can now select your Own materials as Textures in the model selection and assign them to a selected General Variant or Generate Variant.
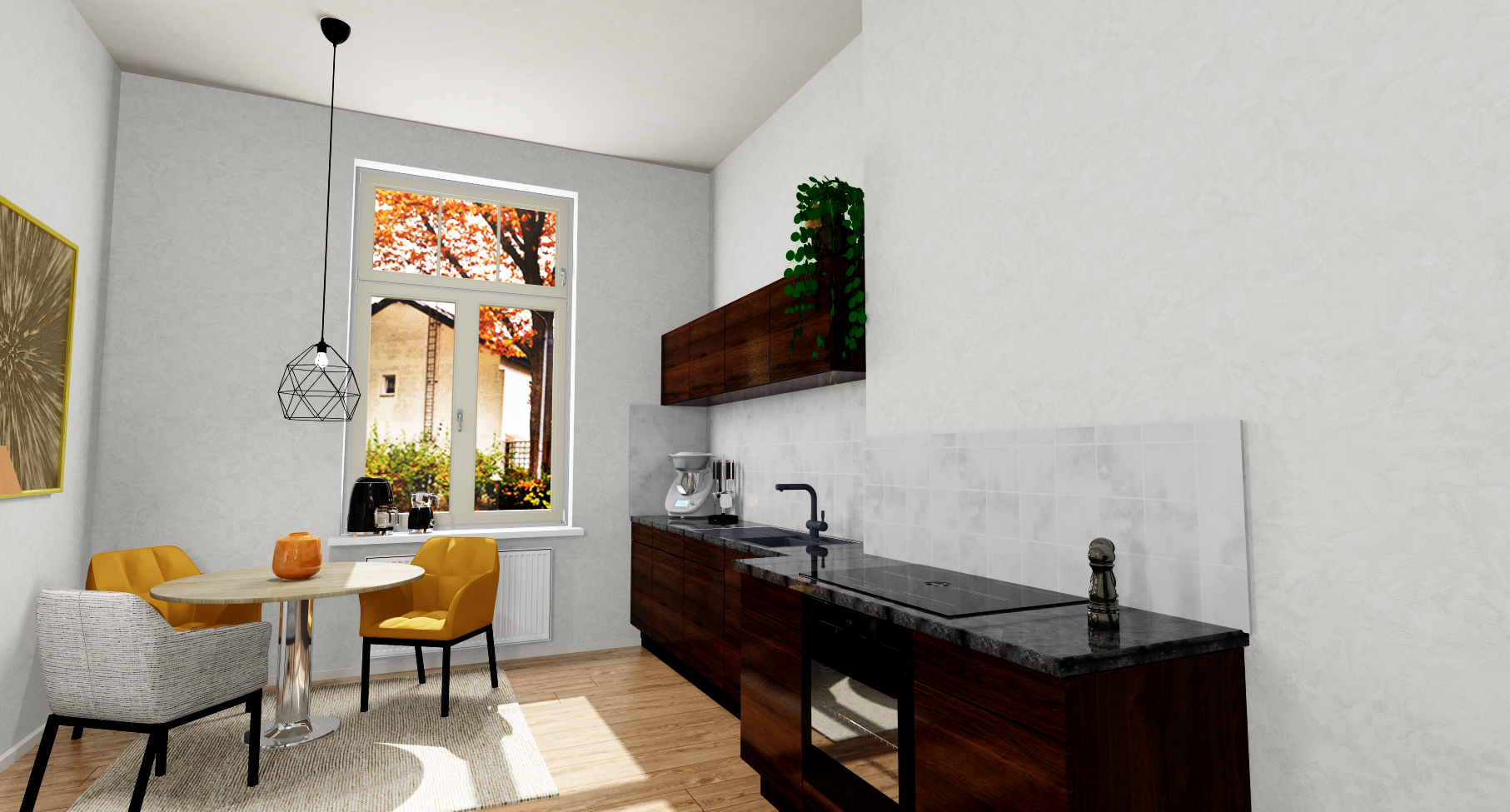
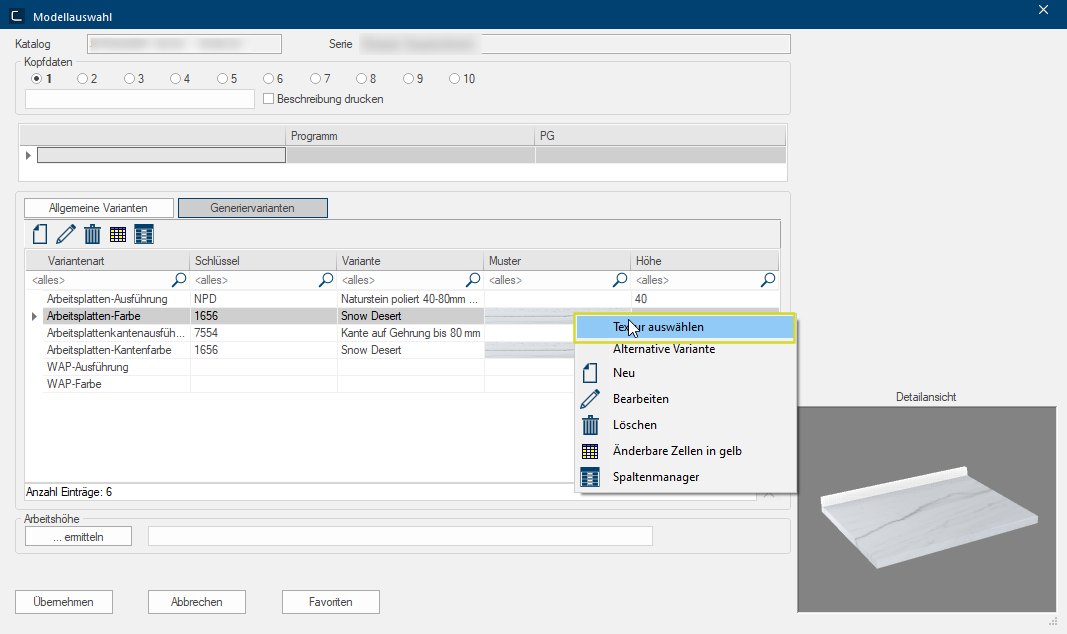
Example: Editing the worktop texture
-
First, in CARAT, switch to the model selection of the catalogue with which you have planned the worktop and, under Pattern, right-click the texture that you want to change and then Select Texture.
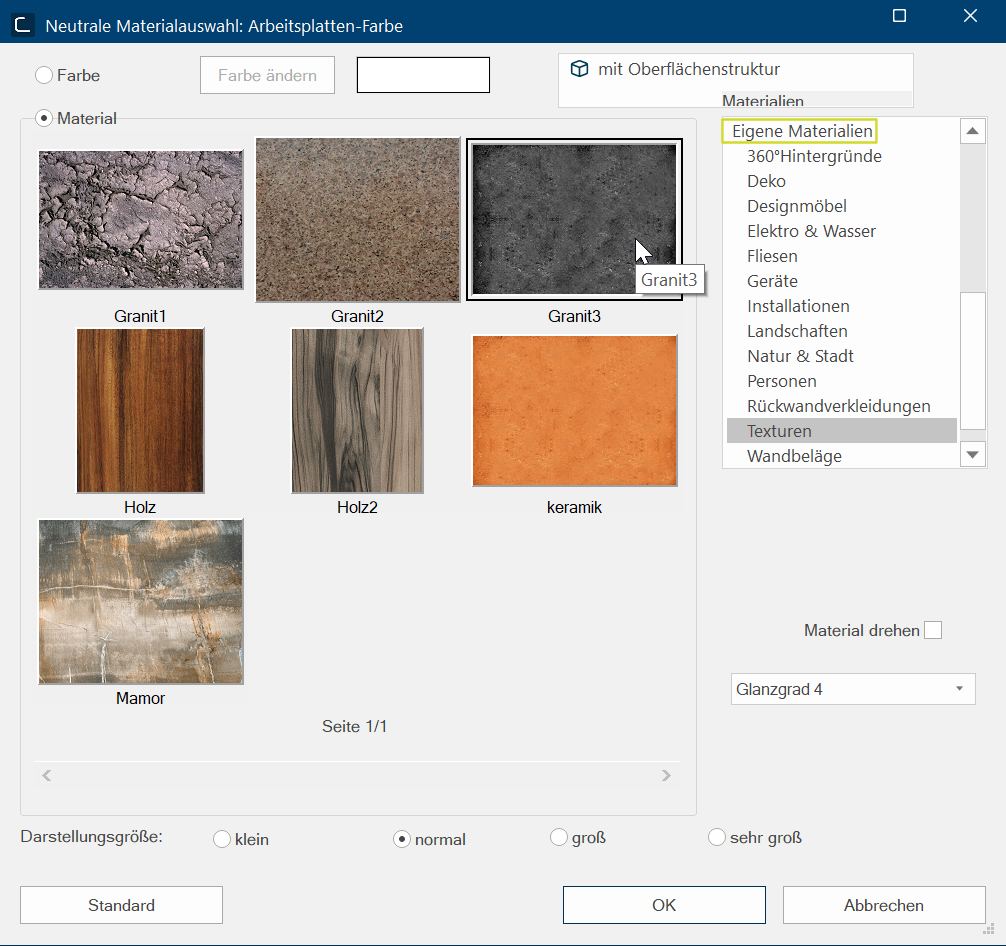
-
The Neutral material selection dialogue opens. Here you select the texture from the Own materials and confirm with OK. Afterwards the changes are visible in the perspective.