The File formats
All computer graphics can be classified into the two main formats The format or formatting (Latin, forma) is designated in word processing as the design of the text document. In this case meaning the selection of character fonts and character style such as bold or italics., raster or vector graphics A vector graphic is a computer image, that is made up of primitive graphics like lines, circles and polygons. For example, to save the image of a circle, a vector graphic requires a minimum of two values: the location of the centre point of the circle, and its diameter.. CARAT offers you several file formats for the export, that all have their pro's and cons. Following we would like to describe the individual file formats in more detail, so that you can find the optimal area of application for the individual graphic formats.
Export formats for raster graphics
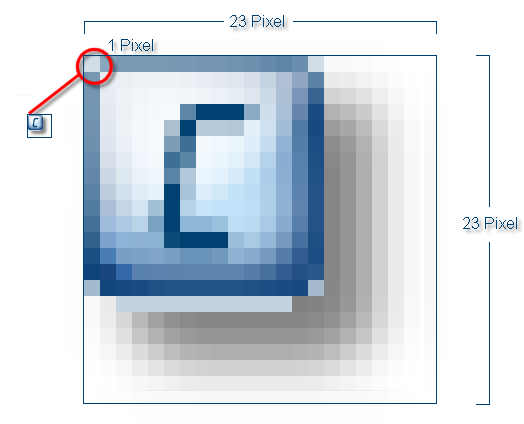
A raster graphic A raster graphic, also named pixel graphic (Bitmap), is a way to describe an image in a data form readable by computers. Raster graphics exist of arrangements of pixels (picture points) in a grid form, each being assigned a colour. The key features of a raster graphic are the width and height in pixels, also know as resolution, as well as the colour depth., also named pixel Pixel or picture element identifies both, the smallest unit of digital raster graphics and the display of these graphics on a monitor with raster activation. graphic (Bitmap), is a way of describing an image in a data form readable by a computer. Raster graphics exist of arrangements of so named pixels (picture points) in a grid form, each being assigned a colour. The key features of a raster graphic are the width and height in pixels, also know as resolution Commonly the picture resolution means the quantity of pixels (picture points), which make up a digital image. Normally values are given in width x height., as well as the colour depth The colour depth is given in bits, and gives information about how many colour tones a single pixel can be assigned. The colour depth indicates thus the refinement of the colour shades.. Raster graphics allow you to show complex images like photos that are not describable using vector graphics (see further below).
Minimalist raster graphics have become a popular art form in the mean while. The spectrum of the so called Pixel art reaches from mobile logo's via web sites up to television spots and advertisement posters. Raster diagrams resemble from their configuration A configuration designates the specific program settings or hardware components in a computer. traditional techniques like mosaic and cross embroidery. The most suitable export formats for raster graphics are: BMP Windows bitmap (BMP) is a two-dimensional raster graphics format, which was developed for the operating system Microsoft Windows and OS/2, and was introduced with Windows 3.0. The file-extension is *.bmp., TIFF TIFF or TIF (Tagged Image File Format) is a file format for saving image data. The TIFF format was originally developed by Aldus (taken over by Adobe in 1994) and Microsoft for scanned raster graphics for colour separation., PNG Portable Network Graphics (PNG) is a graphics format for raster graphics with loss less image compression. Besides different colour depths PNG also supports transparency by alpha. It is an universal, from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recognized format and is supported by all modern web browsers., JPEG JPEG or JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a committee of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) founded in 1986. In September 1992 the committee developed a standardized procedure for a lossy compression of digital (natural) photographic images, that was subsequently named for them. JPEG is the most common photo format on the Web. and PDF The Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF) was developed and perfected in the 80's by Adobe Systems. Adobe PDF files contain data from any application, that can be displayed on every computer, and are suitable thereby to be exchanged with users throughout the world..
Example of a raster graphic
BMP (Windows Bitmap)is a two-dimensional raster graphics format, which was developed for the operating system An operating system is the software which enables the use of a computer. It administrates operating resources like memory, input and output devices and controls the execution of programs. Microsoft Windows and OS/2, and was introduced with Windows 3.0. The file-extension is *.bmp. With the BMP format you can create an individual raster graphic, in any colour depth from black-and-white up to 24-bit colour depth. The bitmap file-format is compatible with other Windows programs and is widespread. However, BMP does not support data compression, which results in large file sizes. Because of this are BMP-files usually not suitable for websites email dispatch. All in all outweigh the disadvantages of the bitmap data-format the advantages.
- Advantages
- BMP supports colour depths from 1 to 24 Bit (max. 16.777.216 colours).
- The BMP-format is widely compatible with existing Windows programs, especially with older versions.
- BMP-files are suitable for Windows background images.
- Disadvantages
- BMP does not support data compression, which results in very large file sizes.
- JPEG or TIFF files are commonly more suitable for pictures in photo-quality.
- BMP is not suitable for websites or email-attachments.
- BMP-files are not supported by web browsers.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a file format, which is able to store a graphic with any colour depth. TIFF is probably the most supported graphic file format in the printing industry. Optional The word option (from Latin: optio = free will) used in computing means a choice. In CARAT it is normally used with a list box. compression is supported, but it is not suitable for being displayed in web browsers. TIFF is, besides PDF, an important format for exchange of data in the pre-press at publishing houses and print shops. Within internet the TIFF-format is used, to provide high-resolution pictures in printable, lossless quality to the users, e.g. publishing houses. Therefore is accepted, that these files have the multiple size than a lossy compressed JPEG-picture.
- Advantages
- Due to its good quality is TIFF foremost suited for print products.
- TIFF is an extensively supported format, especially between Macintosh and Windows computers.
- Optional compression is supported.
- The expandable format supports various optional functions.
- Disadvantages
- TIFF is not supported by web browsers.
- The expandability results in many different TIFF graphic-types.
- Not all TIFF-files are compatible with all programs supporting the basis TIFF-standard.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a format independent from platforms, that supports the greatest possible compression. However this compression is very lossy. The JPEG-compression was developed for natural pictures (raster graphics). These are pictures one finds in the photography or with pictures generated by computers. JPEG is not suitable for digital line drawings (for example for a screenshot or a vector graphics ), which contain many adjoining pixels with exact identical colour values, few colours and sharp edges. For those pictures are the formats BMP, TIFF or PDF better suitable by far.
The grade of compression of JPEG-files can be increased or decreased, however the picture quality is reduced to the benefit of the file size. The JPEG-compression provides good results for photo-realistic picture-material. For simpler picture-material with few colours, sharp contrasts, fixed frames or wide monochromatic areas the JPEG-compression does not produce outstanding results.
- Advantages
- With photographic or photo-realistic picture-material a higher compression is supported.
- The variable In CARAT, variables are wild cards that are used for different values and percent values, since the actual value changes, depending on the respective commission. By employing a variable in a document, for example a text for the VAT, can the VAT amount be supplemented with a wild card. When printing the document, the respective VAT amount will then be displayed in the location of the wild card. compression allows for optimal regulation of the file size.
- JPEG is an extensively supported internet-standard.
- Disadvantages
- This lossy compression leads to a loss of quality of the original picture-data.
- If you modify JPEG-files and store them again, the loss of quality increases compared to the original picture data.
- JPEG is not suitable for simple graphics with few colours, wide monochromatic areas or broad differences of brightness.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is a graphics format for raster graphics with loss less image compression. It was designed as a free replacement of the older, till 2004 with patent claims burdened, GIF format, and is less complex as TIFF. Besides different colour depths PNG also supports transparency by alpha. The PNG format was never patent restricted, as was the case with GIF till 2004 because of the use of LZW algorithm. It is an universal, from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recognized format and is supported by all modern web browsers.
- Advantages
- There are no license fees.
- The compression is loss less and usually more compact as comparable formats.
- Support of True colour (24 Bit colour depth) with a maximum of 48 Bit colour depth.
- Support of Alpha-Transparency (up to 16 Bit, thus 65.536 levels; usual is 8 Bit).
- Support of Colour and Gamma correction technology, to assure the likeliness of images on different systems.
- Disadvantages
- More complexity of the file format compared to GIF.
- As incomplete alternative to GIF-format, it offers no possibilities for animations.
- Does not support the CMYK-Colour model, and is therefore not suitable as full replacement of TIFF.
- With certain types of images (photos) the format achieves by nature not the compression ratio lossy algorithms, such as JPEG.
Export formats for vector graphics
A vector graphic is a computer image, that is made up of primitive graphics like lines, circles and polygons. For example, to save the image of a circle, a vector graphic requires a minimum of two values, the location of the centre point of the circle, and its diameter. Besides the form and position of the primitives, are optionally also the colour, line width, fill pattern and other given data about the appearance be stated.
Contrary to raster graphics, can vector graphics stageless be scaled Scaling is a term in mathematics that designates a size change. In computer graphics the term is used to represent the optimal size of a design on paper., without loosing image quality. With a vector graphic are furthermore the properties of single lines, curves or areas preserved and can also afterwards still be changed. The most suitable export formats for a vector graphic are: EMF EMF (Enhanced Metafile) is a 32-bit-format that can include both vector and bitmap information. It represents an improvement over the 16-bit Windows Metafile (WMF) format. , DXF The Drawing Interchange File Format (DXF) is a file format for the exchange of CAD-files, specified by Autodesk and has been integrated is the CAD-program AutoCAD. The DXF-format has been described by Autodesk and is documented openly. and HPGL The Hewlett Packard Graphic Language (HP-GL) is a printer control language developed by Hewlett Packard for use with pin plotters. Other plotter manufacturers have adopted the HP-GL language for use with their own plotters..
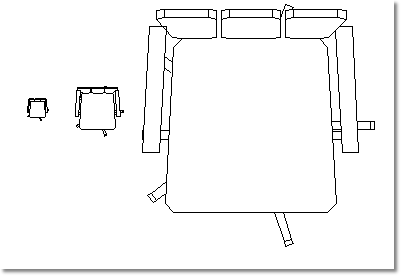
You are shown a vector graphic in the CARAT floor plan as you are also in all other 2D views. An object in a vector graphic can be enlarged or reduced arbitrary (scaled) without loosing quality, as you can recognize from the following picture. On the contrary, depending upon the magnification some details become even more distinct.
Example of a vector graphic
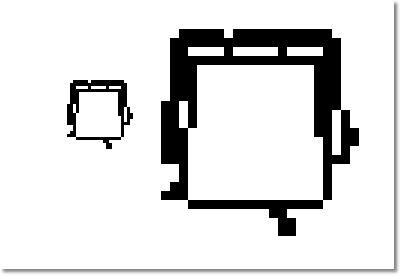
A raster graphic that also has been enlarged, as comparison. As you can see from the picture, the quality decreases significantly when scaling a raster graphic, because the available pixel are only being enlarged.
EMF (Enhanced Metafile) The Enhanced Metafile format is a 32-Bit-format that can include information from a vector graphic as well as from a raster graphic. Windows Enhanced Metafile (EMF) is a further development of Microsoft Windows Metafile Graphic File Format (WMF). It combines any scalable vector graphic with the possibility to use raster graphics as filling. Whilst WMF a 16-bit-format (max. 65536 colours) is, is EMF a 32-bit-format (max. 16777216 colours).
- Advantages
- Expandable file format
- Improved functions in comparison with WMF
- Disadvantages
- The expandability may result in too many different EMF graphic-types.
- Not all EMF-files are compatible to all programs supporting the EMF-standard.
PDF (Portable Document Format) is a platform independent file format for documents, that has been developed by the Firm Adobe Systems and has been released as Acrobat 1, in 1993. With the appropriate programs PDF files can be produced from texts, pictures and graphics, mixed or single, and they can be displayed with appropriate reading programs (most well known Adobe Acrobat Reader DC). A PDF-file can very precisely reproduce documents from the original program including all colours, but also raster graphics or vector graphics. This principally also applies to fonts.
- One of the strong points of the PDF program is, that display programs are available for all popular platforms, so that a platform independent display of the contents is possible. This mean, that when using the appropriate display program, the contents of a PDF-file can be displayed without graphical differences on any type of computer or operating system. PDF is therefore a format to publish contents. Whereas the preparation work is often done in other applications, like CARAT for example, the finished work is released as PDF.
DXF (Drawing Interchange File) is a file format for the exchange of CAD The term CAD stand for Computer Aided Design. All detailed articles from a particular manufacturer, as well as the neutral catalogues in CARAT, are generated with CAD.-files, specified by Autodesk and has been integrated is the CAD-program AutoCAD. The DXF-format has been introduced alongside the DWG-format, to guarantee an external interpretable exchange of data between AutoCAD systems.
The DXF-format has been described by Autodesk and is documented openly. Due to the good documentation and the simple data structure is the DXF-format almost the only program used for data exchange cross-programs, also across different operating systems. Each of today's CAD and CNC-programs can handle the import and export of DXF, which makes DXF as industry standard the common dominator of all CAD systems. All elements useful and implementable for technical drawings are supported in DXF.
- Purpose of use
- This export-format is suitable for all 2D-graphics of CARAT. This graphic-format is especially included for the export of floor plans and front views in CARAT. An CARAT-floor plan, exported as DXF-file, can be read-in in another CAD-application, when required. This could be a planning program of an architect, for example.
HPGL (Hewlett Packard Graphic Language) is a printer control language developed by Hewlett Packard for use with plotters Plotter - The pen plotter is used for designs laid out normally on DIN A3 to A0 size paper. For this it uses an ink pen, that is attached to a carriage. This carriage slides over a rail, that can either shift over the whole paper width (flat bed plotter), or is fixed whereby the paper is shifted over a roller (roll plotter).. Other plotter manufacturers have adopted the HPGL language for use with their own plotters. Although it was not created for that purpose, HPGL has developed into a data exchange format for vector data, because of it's simplicity. The majority of CAD-programs support the export in HPGL-format. A further popular method to create HPGL-data is the "Print to file" while using an appropriate printer driver A device driver, most often shortened driver, is a computer program or module which controls the interaction between attached or built-in devices (hardware). It uses therefore an interface to a communications bus or other communication system that the device is attached to, to send and/or receive control signals and/or data to hardware..