Measure angle

During a planning it can be necessary to be able to measure an angle between two objects exactly. The Angle functions are used for this.
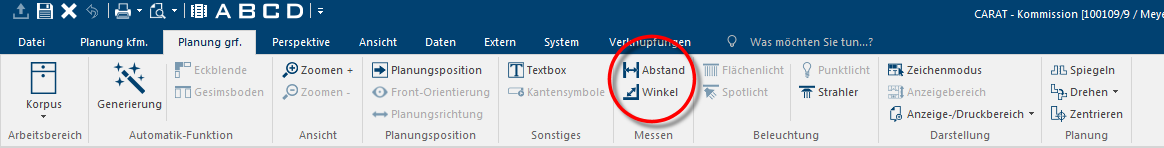
- The Angle functions can be called up directly via the menu ribbon of the Planning graph. index card Some dialogue windows are too voluminous, therefore the functions are separated into indexed groups. The subgroup names typically appear on the tab of the index card at the top of the dialogue and can be selected by clicking on the appropriate tab. in the Measure area.
- When you click Typically the LEFT mouse button is pressed once quickly, if not specified differently. Clicking will either mark an object, or when clicking on a button, the execution of the desired activity (e.g. OK, Cancel, Close). on the Angle option The word option (from Latin: optio = free will) used in computing means a choice. In CARAT it is normally used with a list box. and keep the Ctrl-key The Ctrl-key (short for Control Key) is located on the PC keyboard to the far left in the bottom row of keys. The Ctrl-key has a similar function as the Shift-key. Usually this key is used in conjunction with another key or with the mouse to perform a special function. pressed at the same time, you can directly call up the Measure angle between three points measure options.
|
|
Function |
Action |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Angle |
Only left click Left click + Ctrl-key |
Measuring the angle between two straight lines Measuring the angle between three points |
- In case the dialogue Dialogue, dialogue windows or dialogue fields are special windows in software applications. Dialogue windows are displayed by application programs in different situations to request input or confirmation from the user. is in your way, you can move it very easily by pointing the mouse on the title bar of the dialogue and move the mouse while pressing the left mouse button In dialogue windows you always find one or more buttons that can be activated by clicking on them. Typical functions for buttons are e.g. OK, Cancel, Apply. Buttons are always activated by a single click with the left mouse button.. You can close the dialogue at any time by clicking on the red button Close in the title bar.
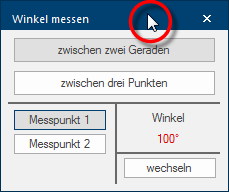
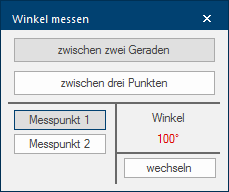
Via this dialogue you have two measuring methods available, with which you can determine an angle if desired. The most commonly used method is probably the determination of an angle Between two straight lines. With the second measuring method, Between three points, you can cover the special cases, where one of both straight lines, for the angle determination, is failing.
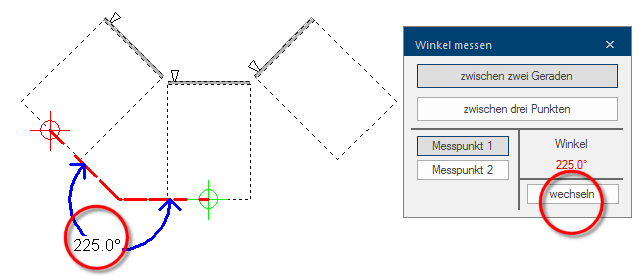
A measured angle will be displayed directly in the graphic as well as directly in the dialogue. You can change the display of the angle between interior angle and exterior angle by using the button Change, beneath the angle specification.
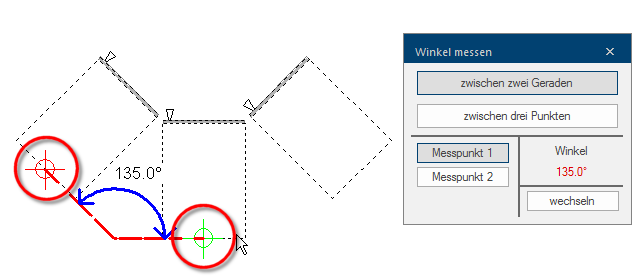
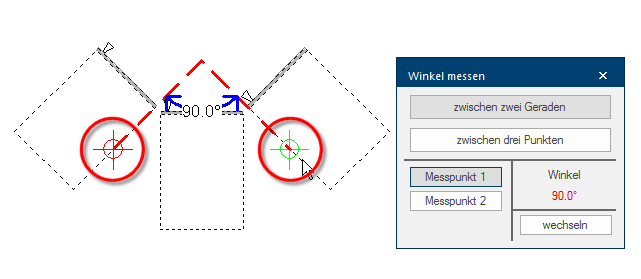
To determine an angle it usually suffices to select two edges in the graphic, between which the angle should be measured. In the following picture are for example the back edges of two adjacent floor units marked for this. The first measuring point will be displayed with a red cross line and the second measuring point with a green one, as you already know from the Measure distance function.
- The selected straight line will be extended by help lines, until they meet at an intersection point. The corresponding angle (usually the interior angle) will be displayed at the intersection point.
- Different angles can be determined, depending on the straight line you select.
- Crucial for this is always only the point where the help lines, as extensions of the straight lines, intersect.
- Upon demand, the display of the angles can also be changed from an interior angle to an exterior angle, by using the Change button.
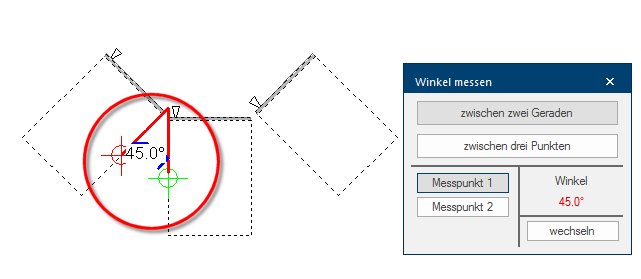
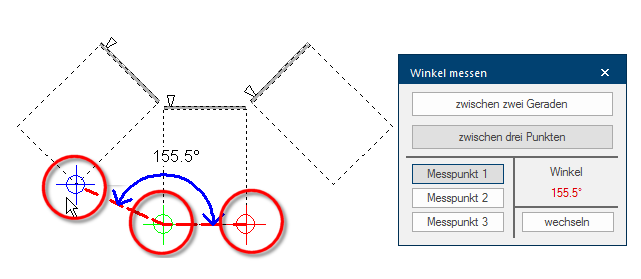
The function for measuring an angle Between three points is especially then useful if you have only one straight line available. In the following picture, the angle for a back wall panelling should be determined.
- For this measuring method it is necessary that measuring point 1 (red cross line) and 2 (green cross line) are placed at the beginning and the end of a straight line, that should be used as point of reference.
- Measuring point 3 (blue cross line) can subsequently be placed on a corner point, that arises from a second straight edge between measuring point 2 and 3. Thus, two straight lines result, with which the angle can be determined.
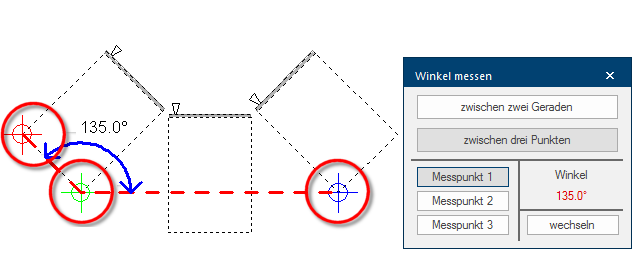
- In the following picture you will see another example, from which you can recognise that you can also determine angles between objects or edges that are father away.